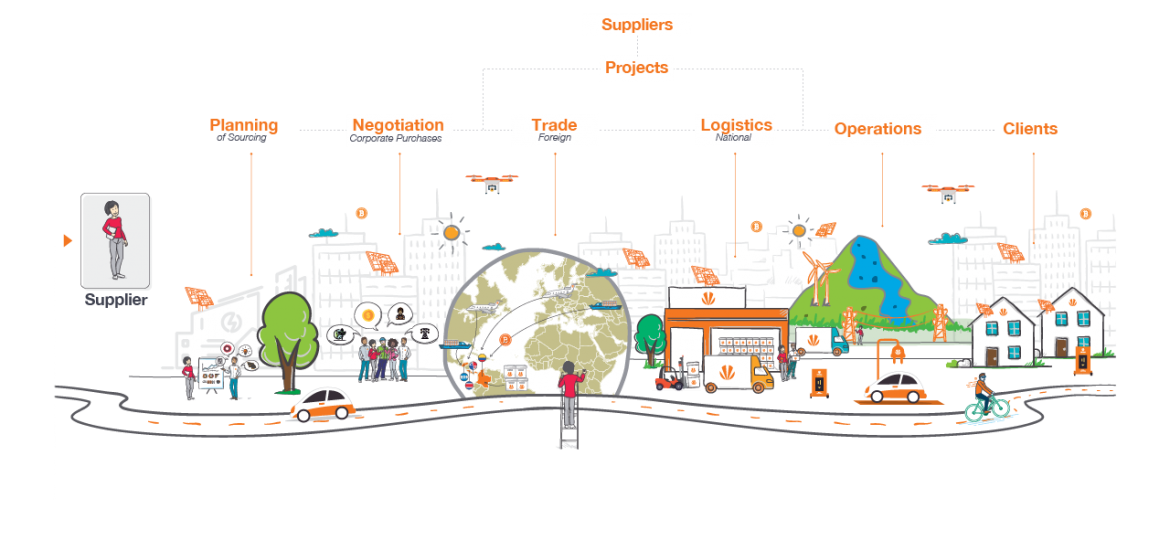
This Is How We Lead
Sustainable Sourcing
Supplier management allows us to mitigate risks, maximize opportunities and procure sustainable supply in the productive chains.

GRI (103-1) Our supply process is strategic and sustainable; it is part of our value chain; it allows mitigating process risks and maximizing opportunities. Our suppliers are allies to whom we give our best to grow together and move forward steadily in the execution of the Company’s strategy.
Our constant goal is to strengthen relationships with suppliers, as key players in the supply process, to continue generating long-term relationships. In this sense, our priority is to ensure the supply and provision of contracted services as part of the Continuity Strategy of our business and of the production chains of which our suppliers – and, in some cases, our clients – are part.
In 2021, we has contractual relationships with 2,814 suppliers; 75% of the total purchases we made were from local suppliers in each country where we operate (Colombia and Central America).
GRI (103-2) We work with suitable suppliers; we carry out due diligence and we have good control of compliance with our policies, codes, manuals and guidelines. Additionally, framed in our Pillars of Supply 4.0 (Digital Transformation) and sustainable supply, we operate under the following principles:
- Strengthening the supply-chain relationship and risk-management model.
- Promoting the simplification and digitization initiatives to enhance the supply-chain transformation and ensure a greater contribution to the business strategy.
- Developing and promoting the action lines that promote the creation of social value for suppliers, to ensure their operation and employability.
- Developing new skills and competencies that allow addressing the challenges and opportunities that arise from mew business models and global trends.
The Supply Chain
GRI (102-9) Contributing to the growth of local suppliers and encouraging the development of the economy of each country where we are present is essential for our Company. For this reason, of the total purchases made in Colombia, Panama, Costa Rica and Honduras during 2021, 75% went to local suppliers in each country where we operate.
At Celsia, we identify risks, based on standard methodologies for comprehensive risk management. The Risk Team deploys the methodology for the entire Company with transversal Probability and Impact Matrices and there is a Risk Manager on each team, who is in charge of applying said methodology.
For the supply chain, the risk-identification process is done annually with permanent monitoring, where a Risk-Identification and Qualification Workshop is carried out for each one. As a result, a report is generated for each of the processes and six Risk Matrices are drawn up, in which action plans focused on risks with a critical, high and moderate rating are subsequently identified, in order to reduce the risk, probability or impact of each. Likewise, the set of controls is evaluated; action-plan monitoring is carried out quarterly.
Critical Suppliers
Critical suppliers are those that provide a high volume of goods or services, critical components or are non-substitutable.
The number of Level 1 critical suppliers decreased, since their characterization methodology varies each year, depending on the management carried out on their suppliers and – given the global context – there are more substitute suppliers.
For Celsia, the high risk in sustainability is one that can affect the development and achievement of the objectives of the Company’s Strategy. These include ESG threats, weaknesses and specific situations to which the Company is exposed. A lack of risk orientation in the supply chain can limit our ability to deliver long-term, sustainable and reliable benefits for all Stakeholders.
Risk Management
Sustainability in the Supply Chain
Target year: 2022
KPI 1
Measure and evaluate ESG Criteria in the Request for Proposals (RFPs) for Contracting Services
Associated Goal
Results in Recent Years
N/A
2018
N/A
2019
KPI 2
% of compliance of the action plans applied to the risks identified in the supply chain.
Associated Goal
Results in Recent Years
KPI 3
% of Supplier satisfaction regarding the management of the supply chain
Associated Goal
Results in Recent Years
In 2021, 1,252 suppliers were evaluated, with which we met our goal of evaluating 35% of our suppliers with ESG criteria.
Priorities in the Supply-Chain Management Strategy
- Continue Strengthening the relationship model with suppliers, to promote collaborative work, integrate them into Celsia’s Strategy and Culture, and enhance their performance and compliance to improve the contribution of our value chain.
- Implement adequate risk management of the supply chain, anticipating the materialization of risks, through the formulation of strategies, definition of controls, monitoring of their application and measurement of their effectiveness.
- Be an ally of change, aligning our Supply 4.0 Strategy to the trends that impact the Company’s business, providing solutions to the main needs of our clients.
- Consider a sustainable supply chain as a fundamental pillar, incorporating a Sustainable Purchasing Policy, focused on the circular economy and good practices of sustainable consumption.
- Transform the operating model to provide efficient, differentiated solutions, leveraging the Company’s growth and the needs of our clients.
Suppliers to which the ESG Evaluation Is Applied
DJSI (1.7.5) GRI (308-1, 414-1) (C-AS2) We have two processes in the Company, which determine the selection of suppliers:
- The pre-selection process represents a weight of 20% in the minimum eligibility criteria for ESG variables.
- The evaluation of the offers that is made on the bidders that participate in a negotiation process represents 25% in the weight of the ESG variables. The criteria applied to the objective selection of suppliers are for bid-request processes.
The ESG (environmental, social and governance) criteria that we take into account for the qualification of our suppliers are:
Financial
(0-10%)
Economic
(35-50%)
Technical
(35-50%)
OHS
(0-10%)
Socio- environmental
(0-10%)
This applies for new and existing suppliers.
ESG Objectives in the Management of the Supply Chain
Comprehensive risk-management in the supply chain
Management and strengthening of Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) topics in our supply chain
OHS management in the supply chain allows us to mitigate business risks and protect the lives of people associated with our value chain.
- We continue to strengthen the I Choose to Take Care of Myself (YEC, in Spanish) program, covering 100% of our suppliers. Additionally, I Choose to Observe (YEO, in Spanish) is applied internally and with our contractors, which will allow opportunities to be identified in time regarding OHS management.
- The program seeks to convert Occupational Health and Safety into a value both in our Organization and in our value chain, favorably impacting the accident severity and frequency rates.
- We also continue to apply the Contractor-Management Model in the different stages of the supply chain: pre-contractual, contractual and post-contractual, which allows us to work on monitoring and providing feedback on the evaluation and development of this Stakeholder group.
The application of the Comprehensive Supplier Risk-Management Model helps us mitigate the risks of the supply chain, to identify opportunities and develop relationship models that adapt to the reality of the business, market effects and obtain the information necessary to define the focus of intervention and supplier development. Likewise, the methodology is useful to assess the risks associated with projects in the supply chain and show weaknesses in processes, to define controls that allow mitigating their probability and impact.
GRI (103-3)
We maintained a 91.4% positive result in the Supplier Satisfaction Survey.
We continued to improve in the comprehensive Risk-Management Survey with suppliers. In 2021, we covered 59 suppliers, which allowed us to assess their risks and the impact on the supply chain.
We had two Talks from Home with our suppliers in June and December, where some of our leaders reported project progress, challenges and, in general, the balance of each period.
We continued with the We Create Social Value Program, launched in 2020 with help lines. Some of these were approved and remain from 2021 as key lines for the development of the program:
- Law of Fair Terms: At Celsia, we advanced the application of the law for MiPymes that are receiving the payment of their invoices, a maximum of 45 days, beginning on January 1, 2021.
- Mentoring: We accompanied 10 suppliers with mentors at the group level.
- Sustainable Confirming: Benefitting more than 7,500 MiPymes at the Business-Group level, with preferential rates and options for our suppliers to choose the one that best suits their needs.
In Logistics, we made progress in having an optimized service model that can serve everyone’s needs in an agile, flexible manner. We focused our efforts on having a logistics infrastructure with greater capacity, robustness, and security. To do this, we implemented the Extended Warehouse Management (EWP) in two warehouses, to improve the efficiency of operations and increase the reliability of inventories.
We complied with the Inventory Schedule, and to be more agile and reliable, we designed an App to carry out physical counts in our own warehouses and in the warehouses of contractors with whom we have reconciliation of materials.
We made 23 relations visits to suppliers of the operation.
We made progress in Phase 2 of the Supplier Development Program, with a focus on sustainable management. We had the participation of 60 companies. At the end of the year, we had the total diagnosis and in 2022, we will continue with the consolidation of the diagnoses, identifying the gaps to work on with experts on each topic.
We obtained an excellent result in the Reputation Study carried out by Invamer, the objective of which was to measure the Company’s reputation and Communication Strategy with our different Stakeholders. The measurement focused on six dimensions. The total result of these dimensions was 93.8, being the highest result among all the Stakeholders evaluated in the Organization.
We evaluated 8% more suppliers in 2021, compared to 2020, within our Performance Measurement Program.
Nuevos desafíos
Estos son nuestros retos en el corto, mediano y largo plazo:
- Continue with the implementation and adjustments of the 4.0 supply strategy, framed in digital transformation, through the automation of high-effort operational processes and decision-making supported by analytics.
- Continue with a second phase in the Supplier Development Program, focused on environmental, social and economic issues.
- Integrate supplier management in the work fronts of sustainable supply: maturity model, supply chain, supplier evaluation model, socialization and inclusion in circular economy, sustainable purchases, socialization of the updating of the contractors manual with environmental aspects.
- Develop an intelligent logistics infrastructure for self-service models, expansion and transfer to warehouses according to the growth and needs of the company.
- Implement prospective models for supply chain management in the face of global markets and strategy implementationnearshoring.
- Implement strategies to strengthen the culture of materials planning in the company.
- Improve the logistics service model to serve the needs of suppliers, contractors and customers with agility and flexibility.
- Improve reliability, inventory indicator and accuracy.
- Implement a comprehensive tool for managing suppliers throughout their life cycle.
- Provide and ensure connectivity models with our suppliers.
- Advance in the strengthening of the digital transformation towards disciplines of blockchain, artificial intelligence and machine learning.
- Develop the management program for strategic allies in the supply chain, in which suppliers become key partners in the business, assuming responsibility for the logistics operation.
- Implement sustainable strategies to adjust the logistics network to the dynamic requirements of the company.
- Incorporate sustainable practices in the chain that allow us to leverage compliance with the company's strategy in a responsible, respectful and profitable manner.
- Leverage new businesses, through sustainable supply models.
- Incorporate virtual processes in the management of the supply chain and flexible and mobile structures with less consumption of working capital.
- Develop and implement fully automated processes, refocusing work teams on strategic processes.
Glosario
Economía circular: At Celsia we understand that the circular economy allows you to think of new designs and business models, identify new products and services and optimize resources to get the most out of our business.
Modelo de madurez: it is the degree to which a company, team or area assimilates or integrates good practices with regard to the management of various programs or projects. It includes various factors, such as measurement tools, evaluation criteria, among others.
Estrategia nearshoring: strategy that seeks supply sources closer to where the need occurs, that is, where the demand is in order to reduce time and costs.